

Ask Why
The Timekeeper’s Enigma: Why 60 Minutes in an Hour?
![]()
As the hands of the clock circle around, dividing our days into neatly segmented portions, one question remains elusive: Why are there 60 minutes in an hour? It’s a mystery that most of us accept without question, but for the inquisitive mind—especially one attuned to the peculiarities of time—this enigma demands investigation. Let’s don our detective hats and delve into the history, mathematics, and cultural influences that led to this seemingly arbitrary division of time.
The Ancient Clues – Sumerian Roots
Every detective begins an investigation by tracing the origins of the mystery, and in this case, our trail leads back thousands of years to the ancient Sumerians. The Sumerians, who lived in what is now modern-day Iraq, were among the first to develop a sophisticated system of mathematics. Their numerical system was based on the number 60, known as the sexagesimal system.
Why 60, you ask? The number 60 is a highly composite number, meaning it has many divisors—1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, and 30. This made it extremely convenient for calculations, trade, and, importantly, timekeeping. The Sumerians, recognizing the utility of 60, began applying it to various measurements, including the division of time.
The Babylonian Connection – Expanding the System
As we follow the trail from the Sumerians, we find ourselves in ancient Babylon. The Babylonians inherited the sexagesimal system and refined it further, using it to create one of the first known astronomical tables. They divided the day into 24 hours, and each hour into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds.
But why did they stick with 60? The answer lies in the heavens. The Babylonians were avid astronomers, and their system of timekeeping was closely linked to their observations of the stars and planets. The number 60 fit neatly into their astronomical calculations, and so it became the standard for measuring time.
The Egyptian Twist – Introducing the 24-Hour Day
No investigation into the mystery of time would be complete without examining the role of ancient Egypt. The Egyptians introduced the concept of dividing the day into 24 parts—12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness—based on their observations of the sun’s movement across the sky.
However, the Egyptians initially didn’t use 60 minutes in an hour. Their timekeeping was more fluid, based on the division of daylight, which varied with the seasons. It wasn’t until later, influenced by Greek and Roman scholars, that the 60-minute hour became standardized. The combination of the Egyptian 24-hour day and the Babylonian 60-minute hour created the timekeeping system we still use today.
The Roman Influence – Time Goes Mechanical
As we sift through historical records, another key player emerges: the Romans. The Romans were instrumental in spreading the 24-hour day and the 60-minute hour across their vast empire. Their influence ensured that this system became the standard across much of the Western world.
But the Romans also added another twist to our story—the invention of the water clock, or “clepsydra.” This early timekeeping device allowed for a more precise measurement of time and helped solidify the 60-minute hour in everyday life. The water clock was a precursor to more advanced mechanical clocks, which would further entrench the 60-minute hour as a universal standard.
The Medieval Revival – Time and the Church
Our investigation now leads us to the medieval period, where the Church played a crucial role in the development of timekeeping. Monasteries required precise timekeeping for prayers and rituals, leading to the development of more accurate mechanical clocks. These clocks were based on the 24-hour day and the 60-minute hour, which by this time had become deeply embedded in both religious and secular life.
The medieval period also saw the introduction of the “horologium,” a timekeeping device that divided the day into equal hours. This innovation helped spread the use of the 60-minute hour even further, solidifying its place in history.
The Mathematical Puzzle – Why Not 100?
As detectives of time, we must now consider an alternative theory: Why not 100 minutes in an hour? In a world where the metric system reigns supreme, the division of time into 60-minute hours seems out of place. Wouldn’t a system based on 10, 100, or 1000 be more logical?
The answer lies in the practical advantages of the number 60. As we discovered earlier, 60 is highly divisible, making it easier to break down into smaller units. In contrast, 100 has fewer divisors, which would make time calculations—especially in a pre-digital age—more cumbersome.
Moreover, the metric system was introduced long after the 60-minute hour had been established, and timekeeping was one area where tradition outweighed the push for decimalization. The 60-minute hour had been deeply ingrained in culture, science, and daily life, making it resistant to change.
The Cultural Inheritance – Modern Timekeeping
As our investigation draws to a close, we find that the 60-minute hour has survived not just because of its mathematical convenience, but also due to its cultural and historical significance. Over millennia, this system has been passed down through civilizations—Sumerian, Babylonian, Egyptian, Greek, Roman—and has become a cornerstone of how we measure and understand time.
In modern times, despite the advent of digital clocks and new technologies, the 60-minute hour remains a universal standard. It’s a testament to the enduring legacy of our ancestors and their innovative approaches to measuring the passage of time.
Conclusion
So, why are there 60 minutes in an hour? The answer is a complex web of history, mathematics, and cultural evolution. From the ancient Sumerians who first recognized the utility of the number 60, to the Babylonians who applied it to time, to the Egyptians and Romans who standardized it, the 60-minute hour is a product of millennia of human ingenuity.
As with any good mystery, the solution lies in the details. The 60-minute hour is not just a random choice, but a carefully considered division of time that has stood the test of centuries. It’s a reminder of how deeply our daily lives are connected to the past, and how even the simplest aspects of our existence—like the ticking of a clock—are shaped by the wisdom of those who came before us.
In the end, our investigation has uncovered not just the reasons behind the 60-minute hour, but also a deeper appreciation for the intricate dance between time, history, and human culture. So the next time you glance at your watch, remember that you’re looking at more than just a measurement of time—you’re looking at the culmination of a mystery that spans thousands of years.
In our article, we’ve seen how a seemingly simple question—why 60 minutes in an hour—opens a portal to a rich history of mathematical brilliance and cultural continuity. This timeless (pun intended) mystery has been solved, but it leaves us with a new understanding of how every tick of the clock connects us to the very foundations of human civilization.
Ask Why
Investing in Hedge Funds: Is It Right for Retail Investors?

![]()
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving financial landscape, millennials across Asia, Europe, and the Americas are increasingly seeking investment opportunities beyond traditional stocks and bonds. Among these options, hedge funds have emerged as a buzzworthy asset class. Known for their sophisticated strategies and potential for high returns, hedge funds have long been associated with institutional investors and ultra-high-net-worth individuals. But is this exclusive investment vehicle suitable for retail investors? This article dives deep into the world of hedge funds, exploring their benefits, risks, and whether they align with the financial goals and risk tolerance of millennial investors.
What Are Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds are pooled investment vehicles that employ a variety of strategies to generate returns for their investors. Unlike mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), hedge funds are not bound by strict regulatory constraints, allowing them to pursue aggressive and unconventional tactics. These strategies may include:
- Long/Short Equity: Betting on both rising and falling stock prices.
- Arbitrage: Exploiting price discrepancies between markets.
- Global Macro: Capitalizing on macroeconomic trends.
- Event-Driven: Profiting from corporate events like mergers or bankruptcies.
The primary goal of hedge funds is to deliver consistent returns regardless of market conditions, often using leverage, derivatives, and other complex instruments. While these strategies can yield impressive results, they also come with significant risks.
Why Hedge Funds Appeal to Millennials
1. Diversification Beyond Traditional Assets
Millennials are known for their desire to diversify their portfolios. With concerns about inflation, geopolitical instability, and volatile stock markets, many are looking for alternative investments that can cushion their portfolios during downturns. Hedge funds offer exposure to non-correlated assets, reducing reliance on traditional equities and bonds.
2. Potential for High Returns
Hedge funds are designed to outperform traditional investments, especially during periods of market turbulence. For millennials eager to grow their wealth quickly, the allure of double-digit annual returns can be tempting.
3. Alignment with Tech-Savvy Values
Many modern hedge funds leverage cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics to inform their strategies. This tech-forward approach resonates with digitally native millennials who value innovation and efficiency.
4. Accessibility Through Platforms
Historically, hedge funds were reserved for accredited investors with substantial capital. However, recent advancements have made them more accessible to retail investors through platforms like Robinhood, eToro, and Fundrise. These platforms allow millennials to invest smaller amounts in hedge fund-like products.
Challenges of Investing in Hedge Funds
While hedge funds offer exciting possibilities, they are not without drawbacks. Here’s what millennial investors should consider before diving in:
1. High Fees
Hedge funds typically charge a “2 and 20” fee structure—2% of assets under management (AUM) and 20% of profits. For retail investors with limited capital, these fees can eat into returns significantly, making it harder to achieve meaningful gains.
2. Lack of Transparency
Unlike publicly traded securities, hedge funds operate with minimal disclosure requirements. Investors often have limited visibility into the fund’s holdings, strategies, and performance metrics, which can make it difficult to assess risk.
3. Illiquidity
Most hedge funds require investors to lock up their money for extended periods, ranging from one to several years. This lack of liquidity can be problematic for millennials who prioritize flexibility and accessibility.
4. Higher Risk Profile
Hedge funds use aggressive strategies that can amplify losses as well as gains. For example, excessive leverage or poorly timed bets can lead to catastrophic outcomes. Retail investors must carefully evaluate whether they can stomach such volatility.
5. Regulatory Concerns
Although regulations vary by region, hedge funds generally face less oversight than mutual funds or ETFs. This increases the potential for fraud or mismanagement, particularly in emerging markets.
Are Hedge Funds Suitable for Retail Investors?
The short answer is: it depends. While hedge funds offer unique advantages, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Let’s break down the factors that determine their suitability for millennial investors.
1. Financial Goals
If your primary objective is long-term wealth accumulation, low-cost index funds or ETFs might be a better fit. On the other hand, if you’re comfortable taking on higher risk for potentially outsized rewards, hedge funds could complement your portfolio.
2. Risk Tolerance
Hedge funds thrive on complexity and uncertainty. If you’re risk-averse or prefer straightforward investments, steer clear of this asset class. Conversely, adventurous millennials with a strong appetite for risk may find hedge funds appealing.
3. Investment Horizon
Given the illiquid nature of most hedge funds, they are best suited for investors with a medium- to long-term horizon. If you anticipate needing access to your funds within the next few years, consider more liquid alternatives.
4. Capital Availability
Although some platforms now cater to retail investors, minimum investment thresholds for hedge funds remain relatively high compared to other asset classes. Ensure you have sufficient disposable income before committing.
Alternatives to Direct Hedge Fund Investments
For millennials hesitant to dive directly into hedge funds, there are alternative ways to gain exposure to similar strategies:
1. Hedge Fund ETFs
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that replicate hedge fund strategies provide a cost-effective way to access diversified portfolios without the high fees or lock-up periods.
2. Managed Futures Accounts
These accounts mimic global macro strategies used by hedge funds but are available to retail investors at lower costs.
3. Robo-Advisors with Alternative Allocations
Some robo-advisors incorporate alternative investments, including hedge fund-like strategies, into their portfolios. Examples include Betterment and Wealthfront.
4. Crowdfunding Platforms
Platforms like AngelList and Republic allow retail investors to participate in venture capital and private equity deals, offering hedge fund-like opportunities with lower barriers to entry.
Tips for Millennial Investors Considering Hedge Funds
If you decide to explore hedge funds, keep the following tips in mind:
1. Do Your Research
Thoroughly vet any hedge fund or platform before investing. Look for track records, manager expertise, and independent reviews.
2. Start Small
Begin with a modest allocation to gauge how hedge funds perform within your portfolio. Avoid putting all your eggs in one basket.
3. Understand the Fees
Factor in management and performance fees when calculating potential net returns. Compare these costs against simpler, cheaper alternatives.
4. Seek Professional Advice
Consult a financial advisor familiar with alternative investments to ensure hedge funds align with your overall strategy.
5. Stay Informed
Keep abreast of market trends and economic developments that could impact hedge fund performance. Regular monitoring will help you make informed decisions.
Conclusion: Weighing the Pros and Cons
Hedge funds represent a tantalizing opportunity for millennial investors seeking diversification, innovation, and potentially high returns. However, their high fees, illiquidity, and elevated risk profile make them unsuitable for everyone. Before jumping in, ask yourself: Are you willing to accept the trade-offs? Do you have the financial stability and risk tolerance required?
For those who do proceed, remember that hedge funds should supplement—not dominate—your portfolio. By combining them with traditional assets and alternative investments, you can build a balanced portfolio tailored to your unique needs and aspirations.
As the saying goes, “Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.” Whether you choose to invest in hedge funds or explore other avenues, the key is to stay informed, remain disciplined, and focus on long-term growth. After all, smart investing isn’t just about chasing quick wins—it’s about building a sustainable future.
Your journey to financial success starts with knowledge. Will hedge funds play a role in yours?
Ask Why
The Case of Hitler’s Hatred: Unraveling the Mystery of Anti-Semitism

![]()
Alright, buckle up, because we’re diving deep into one of history’s darkest and most perplexing cases: Why did Adolf Hitler hate Jewish people? This isn’t your average detective story—this one’s got layers upon layers of twisted ideology, personal grudges, and societal manipulation. But don’t worry, we’ll break it down step by step, detective-style, so you can follow along and make sense of the madness.
Clue #1: The Historical Backdrop
To crack this case, we need to first understand the scene where it all went down—early 20th century Europe. Anti-Semitism, or hatred against Jews, wasn’t something Hitler invented. This prejudice had been festering in Europe for centuries. Back in the Middle Ages, Jews were often scapegoated for all sorts of social and economic issues. Whenever there was a plague, a financial crisis, or even bad weather, people were quick to blame the Jewish community.
By the time Hitler came onto the scene, anti-Semitism was already embedded in many European societies. So, while Hitler didn’t start the fire, he sure knew how to pour gasoline on it.
Clue #2: Hitler’s Early Life
Let’s rewind to Hitler’s early years. Born in 1889 in Austria, young Adolf didn’t have the easiest childhood. His family life was turbulent—his father was strict and his mother overprotective. He was a mediocre student and didn’t get into art school, which was his dream. So, where does the Jewish hatred fit into all this?
There’s no solid evidence that Hitler had any strong anti-Semitic views in his youth. In fact, there were Jews who supported his art aspirations, and Vienna, where he lived for a time, was a multicultural city. But as Hitler struggled with poverty and failure, he started to internalize some of the toxic ideas that were floating around in society.
Clue #3: World War I and the “Stab-in-the-Back” Myth
Now, let’s fast forward to World War I. Hitler served as a soldier in the German army, and the defeat of Germany in 1918 hit him hard. Like many Germans, he was shocked by the loss and devastated by the harsh terms of the Treaty of Versailles. But here’s where it gets interesting—Hitler didn’t just blame the defeat on military failure. He bought into a conspiracy theory known as the “stab-in-the-back” myth.
According to this myth, Germany didn’t lose the war on the battlefield; instead, it was betrayed from within by “unpatriotic” elements—particularly Jews, communists, and socialists. Never mind that there was no real evidence to support this; the myth was a convenient scapegoat. For Hitler, it was the perfect explanation for why things had gone so wrong. And thus, the seeds of his anti-Semitism were planted deeper.
Clue #4: The Rise of Nazi Ideology
As Hitler climbed the political ranks in the 1920s, he began to articulate his ideas more clearly, especially in his book Mein Kampf (My Struggle). Here, Hitler lays out a twisted worldview where history is seen as a racial struggle for survival. He believed in the superiority of the “Aryan” race and saw Jews as the ultimate enemy—parasitic, destructive, and bent on world domination.
Why the Jews? Hitler’s thinking was a toxic mix of pseudo-scientific racism, existing anti-Semitic stereotypes, and a deep-seated need to blame someone for Germany’s problems. He saw Jews as both racially inferior and a powerful force conspiring against Germany. It’s a contradiction, sure, but it’s one that Hitler and his followers clung to with dangerous conviction.
Clue #5: The Economic and Political Context
But ideology alone doesn’t explain why Hitler’s anti-Semitism gained traction. The context in which he rose to power is key. Germany in the 1920s and 1930s was a mess—economic crises, hyperinflation, and massive unemployment had created a breeding ground for extremist ideas. People were desperate for a solution, and Hitler offered them one, wrapped in nationalist rhetoric and backed by the scapegoating of Jews.
The Nazis blamed Jews for everything from economic hardship to cultural decline. And as Hitler rose to power in 1933, these ideas weren’t just fringe beliefs anymore—they became state policy. Anti-Semitism became institutionalized, leading to the horrific events of the Holocaust, where six million Jews were systematically murdered.
Clue #6: Personal Grudges and Paranoia
Now, let’s not forget that Hitler was a deeply paranoid individual. Some historians suggest that his hatred of Jews might have also been influenced by personal experiences—failed ambitions, jealousy, or even illness. But at the end of the day, whether it was personal or ideological, Hitler’s anti-Semitism was extreme and unwavering.
It’s important to note that Hitler wasn’t alone in his hatred. Many Germans, whether out of fear, propaganda, or genuine belief, supported or at least went along with Nazi policies. This complicity allowed Hitler to turn his twisted ideas into a genocidal reality.
The Final Verdict: The Danger of Ideology
So, why did Hitler hate Jewish people? The answer isn’t simple, but it boils down to a mix of historical anti-Semitism, personal failures, political opportunism, and a dangerous ideology that portrayed Jews as the root of all evil. Hitler’s anti-Semitism wasn’t just a personal grudge—it was a core part of his worldview and the Nazi agenda.
But here’s the thing—Hitler’s hatred didn’t exist in a vacuum. It was nurtured by a society that had long been steeped in prejudice and fear. And that’s the real lesson here. When hate goes unchecked, when prejudice is allowed to fester, it can lead to unimaginable horrors.
Detective’s Closing Thoughts: Lessons for Today
As we close this case, it’s crucial to remember that history has a way of repeating itself if we’re not careful. The rise of Hitler and the Holocaust are reminders of the dangers of unchecked hate and the power of destructive ideologies.
Today, we see echoes of this in various forms of discrimination and racism around the world. The key takeaway? Stay vigilant, question the narratives that blame entire groups for society’s problems, and never let hatred take root. Because once it does, it can grow into something truly monstrous.
So, there you have it—an investigation into one of history’s darkest chapters. The case of Hitler’s hatred is one that we must never forget, and it’s up to us to ensure that the lessons learned are passed down through generations. Stay curious, stay informed, and most importantly, stay human.
Ask Why
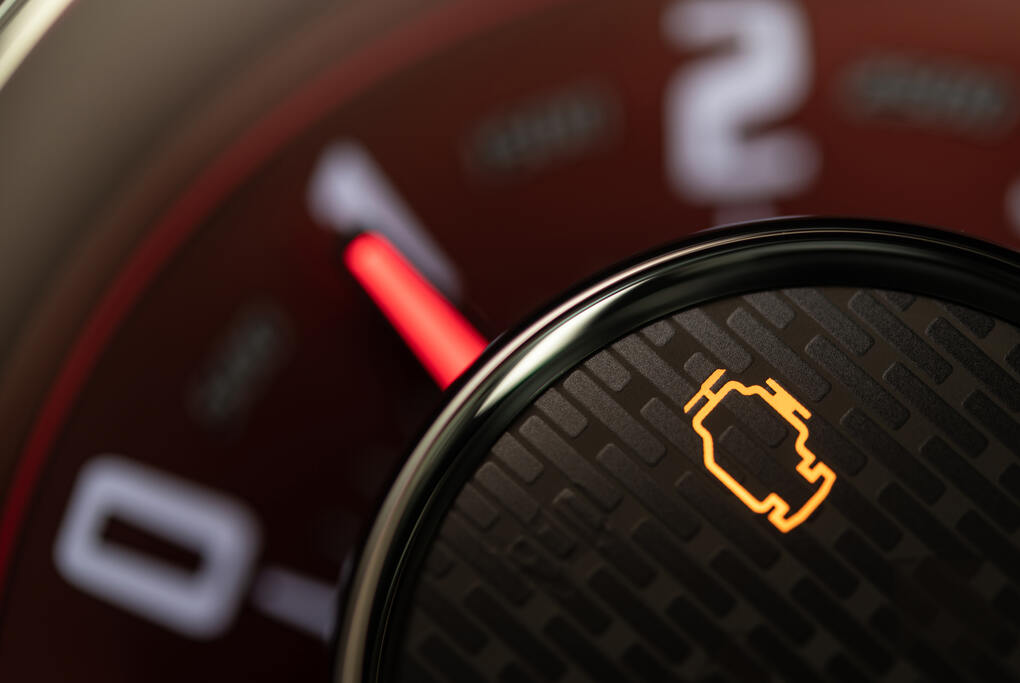
Why Is the Check Engine Light On? A Detective’s Guide to Unraveling the Mystery

![]()
It was a quiet evening when my phone rang—a low, persistent buzz that interrupted the silence like the ominous glow of a check engine light on a dimly lit dashboard. I answered, and the voice on the other end was frantic, panicked even. “Detective, I need your help. My check engine light just came on, and I don’t know what to do.”
I leaned back in my chair, the soft creak of leather echoing in the stillness. The check engine light—a small, innocuous symbol that strikes fear into the hearts of many. To some, it’s a minor inconvenience, but to a seasoned detective like myself, it’s the beginning of a case that could unravel in countless ways. Each possibility a thread to be followed, each outcome a puzzle piece waiting to be placed.
“Calm down,” I said, my voice steady and measured. “This isn’t the time to panic. It’s time to investigate.”
Let me walk you through the process of uncovering the truth behind that dreaded light. Together, we’ll piece together the clues and get to the bottom of this mechanical mystery.
Step 1: The Initial Observation (Understanding the Check Engine Light)
First, we need to understand what we’re dealing with. The check engine light is like a tip-off in a criminal case—a warning that something isn’t quite right under the hood. It could be something minor, like a loose gas cap, or it could be a sign of a more serious issue. But before we jump to conclusions, we need to gather the facts.
“When did you first notice the light?” I asked, jotting down notes as if taking a statement from a witness.
“It just came on out of nowhere,” the caller replied, their voice tinged with anxiety.
“Good,” I muttered. “Now, let’s consider the possibilities.”
Step 2: The Usual Suspects (Common Causes of the Check Engine Light)
In any investigation, there are always the usual suspects—those who are more likely to be involved based on prior knowledge and evidence. The check engine light is no different. There are a few common culprits that could be responsible, and it’s our job to identify them.
- Loose or Faulty Gas Cap: One of the most common reasons for the check engine light to come on is a loose or faulty gas cap. It’s like catching a petty thief—a minor issue that can cause big headaches if not addressed. The gas cap seals the fuel system, and if it’s not properly tightened, it can trigger the light.“Check your gas cap,” I instructed. “Make sure it’s on tight.”
- Oxygen Sensor Malfunction: The oxygen sensor monitors the amount of unburned oxygen in your car’s exhaust and sends the data to the car’s computer. If it’s not working correctly, the car’s performance could be compromised. Think of it as a witness who’s feeding you false information.“If the gas cap isn’t the problem, we might be dealing with a faulty oxygen sensor,” I noted.
- Catalytic Converter Issues: The catalytic converter is part of your car’s exhaust system. It helps reduce harmful emissions, making it a key player in the environmental game. But if it’s damaged or not working properly, the check engine light will come on. This is like finding out one of your prime suspects has a shady background.“A malfunctioning catalytic converter can be costly,” I said. “But it’s essential to address it.”
- Mass Airflow Sensor Problems: The mass airflow sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine, helping the car’s computer determine the correct fuel-to-air ratio. If it’s malfunctioning, the engine could be running too rich or too lean, causing the check engine light to illuminate. It’s like getting the wrong intel—it throws everything off balance.“This could affect your car’s fuel efficiency,” I explained, “which is why it’s important to get it checked out.”
- Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Issues: Spark plugs and ignition coils are essential for the combustion process in your engine. If they’re not working properly, the engine may misfire, triggering the check engine light. It’s like having an unreliable partner in a stakeout—you never know when they’re going to mess things up.“A misfire can lead to more serious engine problems,” I warned. “Don’t ignore this one.”
Step 3: Gathering the Evidence (Diagnosing the Issue)
Now that we’ve identified the usual suspects, it’s time to gather more evidence. In the world of automotive diagnostics, this means using an OBD-II scanner—a tool that reads the error codes stored in your car’s computer. These codes act like fingerprints at a crime scene, pointing us in the direction of the problem.
“If you have an OBD-II scanner, now’s the time to use it,” I advised. “If not, take your car to a mechanic or an auto parts store—they can usually check the codes for you.”
The scanner will produce a code, a combination of letters and numbers that corresponds to a specific issue. It’s like decoding a secret message—once you know what the code means, you’re one step closer to solving the case.
Step 4: Interpreting the Evidence (Understanding the Codes)
Once we have the code, it’s time to interpret the evidence. Each code corresponds to a different issue, and understanding what it means is crucial to resolving the problem.
For example:
- P0171: This code indicates that the engine is running too lean (not enough fuel). It could be caused by a vacuum leak, a clogged fuel filter, or a malfunctioning oxygen sensor.
- P0420: This code suggests that there’s an issue with the catalytic converter’s efficiency. It might be due to a failing catalytic converter, or it could be the result of an exhaust leak.
- P0300: This code indicates a random or multiple cylinder misfire. The cause could be faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or even a fuel delivery issue.
“It’s like reading between the lines of a suspect’s testimony,” I said, as I deciphered the codes. “Each one tells us something different, but together, they paint a clearer picture.”
Step 5: Taking Action (Fixing the Problem)
With the evidence in hand and the problem identified, it’s time to take action. This is where the real work begins—rolling up your sleeves and getting your hands dirty. Depending on the issue, you might be able to fix it yourself, or you might need to call in a professional.
- Gas Cap: If the problem is a loose or faulty gas cap, simply tightening or replacing it should do the trick. Once it’s secured, the check engine light may turn off after a few driving cycles.
- Oxygen Sensor: If the oxygen sensor is the culprit, replacing it should resolve the issue. It’s a relatively simple fix, but if you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, a mechanic can handle it.
- Catalytic Converter: A damaged catalytic converter is a more serious problem. It may need to be replaced, which can be expensive. But ignoring it could lead to bigger problems down the road.
- Mass Airflow Sensor: If the mass airflow sensor is malfunctioning, cleaning or replacing it should solve the problem. This is another fix that a mechanic can easily handle.
- Spark Plugs or Ignition Coils: Replacing faulty spark plugs or ignition coils can restore your engine’s performance and turn off the check engine light. It’s a straightforward job, but one that requires the right tools and knowledge.
Step 6: Closing the Case (Clearing the Code)
Once the problem is fixed, the final step is to clear the error code from the car’s computer. This can be done with an OBD-II scanner or by driving the car for a while—the light should turn off on its own after a few successful trips.
“Remember,” I cautioned, “just because the light is off doesn’t mean the case is closed. Keep an eye on your car’s performance, and if the light comes back on, don’t ignore it.”
Final Thoughts: The Detective’s Conclusion
And there you have it—a step-by-step guide to solving the mystery of the check engine light. Like any good detective, you need to approach the problem methodically, gather the evidence, and take action based on the facts. Whether it’s a minor issue like a loose gas cap or a more serious problem like a failing catalytic converter, understanding the root cause is key to keeping your car running smoothly.
In the world of automotive mysteries, the check engine light is just another case waiting to be solved. And with the right tools and a bit of detective work, you can crack the case every time. So, the next time that little light flickers on, don’t panic—just remember the steps, follow the clues, and you’ll be back on the road in no time. After all, every detective knows that even the smallest light can lead to the biggest breakthroughs.
-

 Top 1011 months ago
Top 1011 months agoUnmasking the Cruelty: Top 10 Ways to Prevent Animal Cruelty
-

 Ask Why11 months ago
Ask Why11 months agoWhy Is the Check Engine Light On? A Detective’s Guide to Unraveling the Mystery
-

 How-Tos11 months ago
How-Tos11 months agoUnmasking the Mystery of Keeping Squirrels Away
-

 Top 1011 months ago
Top 1011 months agoUnmasking the Threats: The Top 10 Ways to Protect Endangered Species
-
 Forex7 months ago
Forex7 months agoWhat Are Swing Highs and Swing Lows in Market Structure? A Comprehensive Guide for TradingView Users
-

 Head To Head11 months ago
Head To Head11 months ago10 Reasons Why Dogs Are Better Than Cats: A Detective’s Investigation
-

 Deep Science11 months ago
Deep Science11 months agoThe 10 Craziest Scientific Discoveries You Missed in 2024
-

 Deep Science11 months ago
Deep Science11 months agoCatch the Perseid Meteor Shower: Peak Viewing Tips!
